
Neutron star or black holeĭepending on the mass at the start of its life, a supernova will leave behind either a neutron star or a black hole.

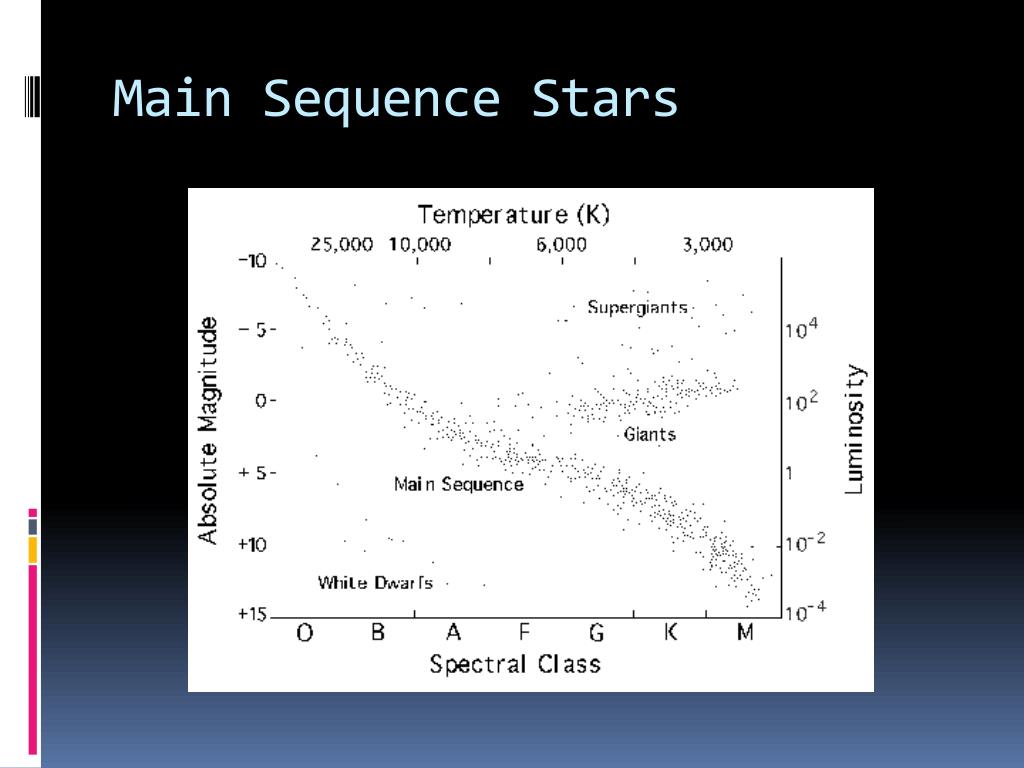
SupernovaĪ larger star with more mass will go on making nuclear reactions, getting hotter and expanding until it explodes as a supernova.Īn exploding supernova throws hot gas into space. In this instance, the star becomes a white dwarf which fades and changes colour as it cools. So, if you can determine the main-sequence lifetime of a B6 star, you will have estimated the age of the Pleiades. These B6 stars will be the next to move off, and they are just ending their main-sequence lifetimes. When all the nuclear reactions are over, a small star like the Sun may begin to contract under the pull of gravity. The most massive stars that are still on the main-sequence are of spectral type B6. When all the hydrogen has been used up in the fusion process, larger nuclei begin to form and the star may expand to become a red giant. The Sun is at this stable phase in its life. Main sequence starĭuring this stable phase in the life of a star, the force of gravity holding the star together is balanced by higher pressure due to the high temperatures. The fusion process releases energy, which keeps the core of the star hot. A star is formed when it is hot enough for the hydrogen nuclei to fuse together to make helium. ProtostarĪs the mass falls together it gets hot. Gravity begins to pull the dust and gas together. Main sequence star: a star 0. Red super giant star \(\rightarrow\) supernova \(\rightarrow\) neutron star, or a black hole (depending on size) A nebulaĪ star forms from massive clouds of dust and gas in space, also known as a nebula. Stars that are far greater in mass than the Sun follow the right hand path: Red giant star \(\rightarrow\) white dwarf \(\rightarrow\) black dwarf Stars that are a similar size to the Sun follow the left hand path: Following this, stars develop in different ways depending on their size. For a newborn star, have an orange light inside a 3-inch globe. A cloud of dust and gas, also known as a nebula, becomes a protostar, which goes on to become a main sequence star. To show the birth of a star as a hot gas cloud, wrap the outside of a globe in cotton and place it over the first bulb of the string of lights. These stars must have been formed relatively recently. The diagram shows the life cycles of stars that are:Īll stars begin life in the same way. A supergiant star such as Antares, a bright main-sequence star such as Rigel, or even a more modest star such as Sirius cannot have endured as long as the Sun has endured. The life cycle for a particular star depends on its size.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
